Abstract
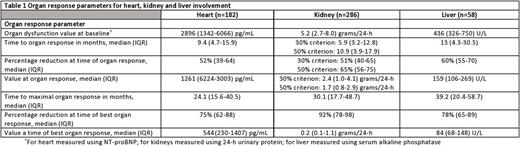
Introduction: Organ recovery following anti-plasma cell therapy is associated with an improved outcome in patients with AL amyloidosis. However, unlike hematological response criteria, organ response criteria are graded only as present or absent, without taking into consideration the depth of organ response. Monoclonal antibodies targeting the amyloid deposits are emerging as a potential therapeutic modality to enhance organ recovery. Therefore, more exact grading of organ response may help in selection of patients who may benefit from immune-mediated therapies. Methods: Patients were included if they had biopsy-proven systemic AL amyloidosis seen within 90 days of diagnosis, between 2000 and 2015. Patients had to have involvement of at least one assessable organ (heart, kidney or liver) and documentation of organ response per consensus criteria. Time to organ response and time to best organ response (defined as the lowest level of biochemical dysfunction, prior to hematological progression or institution of second line therapy) were calculated from date of first line therapy. Results: Four hundred and sixteen patients are included. Patients had a median of 1 assessable organ for response [interquartile range (IQR) 1-2]. Summary of organ response parameters is presented in Table 1. One hundred and eighty two patients were evaluable for cardiac response. Time from treatment initiation to achievement of cardiac response was 9.4 months (IQR 4.7-15.9). The median maximal reduction in NT-proBNP from baseline was 75% (IQR 62-88%) with a median nadir level of 544 pg/mL. The median time to maximal cardiac response was 24.1 months (IQR 15.6-40.5). The lower the NT-proBNP trough level achieved, the better the survival, both if assessed by percentage reduction from baseline as well as the nadir level. However, in patients with a baseline NT proBNP >2000 pg/mL survival was improved when the lowest NT proBNP was below 500 pg/mL rather than a >90% reduction. Two-hundred and eighty six patients were evaluable for renal response. Time to reduction of 30% and 50% in urinary protein was 5.9 and 10.9 months, respectively. Median maximal reduction in urinary protein from baseline was 92% (IQR 78-98%), to a median nadir value of 0.2 gr/24-h (IQR 0.1-1.1). Median time to maximal reduction in urinary protein was 30.1 (IQR 17.7-48.7) months. In patients with renal and no cardiac involvement (n=147), the greater the urinary protein reduction, the better the overall survival. Fifty eight patients were evaluable for hepatic response. The median time to hepatic response was 13 (IQR 4.3-30.5) months. The median maximal reduction in serum alkaline phosphatase (AP) was 78% (IQR 65-89%) with a median nadir level of 84 U/L. The median time to maximal hepatic response was 39.2 (IQR 20.4-58.7) months. Patients with hepatic response who achieved greater than 75% reduction in baseline AP had improved survival compared to patients with hepatic response at a 50-75% reduction in AP (median survival 179 vs 90.8 months, respectively). Conclusion: Grading the depth of organ response provides better prognostic information for patients with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis. In all organs (heart, kidney, liver), the deeper the organ response, the better the survival. This should lead to a refinement in organ response criteria to include increasing depths of organ response rather than a dichotomous outcome of response versus no response. Deep organ responses are more common in patients with renal and hepatic involvement than cardiac involvement.
Dispenzieri: Celgene, Millenium, Pfizer, Janssen: Research Funding. Kapoor: Takeda, Celgene and Amgen: Research Funding. Russell: Imanis Life Sciences: Equity Ownership; Vyriad: Equity Ownership. Kumar: Celgene, Millennium/Takeda, Onyx, AbbVie, Janssen, Sanofi, Novartis, Amgen, Genentech, Merck, Oncopeptides, Roche, Skyline Diagnostics: Research Funding; Celgene, Millennium, BMS, Onyx, Janssen, Noxxon, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Oncopeptides, Skyline Diagnostics, Takeda: Consultancy; Skyline: Honoraria. Gertz: Millennium: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene, Novartis, Smith-Kline, Prothena, Ionis, Amgen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal